Portal:Asia

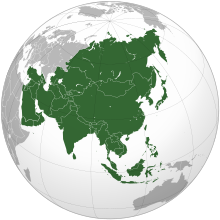 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ ⓘ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, as well as many other religions. (Full article...) Featured article The Temple of Eshmun (Arabic: معبد أشمون) is an ancient place of worship dedicated to Eshmun, the Phoenician god of healing. It is located near the Awali river, 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) northeast of Sidon in southwestern Lebanon. The site was occupied from the 7th century BC to the 8th century AD, suggesting an integrated relationship with the nearby city of Sidon. Although originally constructed by Sidonian king Eshmunazar II in the Achaemenid era (c. 529–333 BC) to celebrate the city's recovered wealth and stature, the temple complex was greatly expanded by Bodashtart, Yatonmilk and later monarchs. Because the continued expansion spanned many centuries of alternating independence and foreign hegemony, the sanctuary features a wealth of different architectural and decorative styles and influences. The sanctuary consists of an esplanade and a grand court limited by a huge limestone terrace wall that supports a monumental podium which was once topped by Eshmun's Greco-Persian style marble temple. The sanctuary features a series of ritual ablution basins fed by canals channeling water from the Asclepius river (modern Awali) and from the sacred "YDLL" spring; these installations were used for therapeutic and purificatory purposes that characterize the cult of Eshmun. The sanctuary site has yielded many artifacts of value, especially those inscribed with Phoenician texts, such as the Bodashtart inscriptions and the Eshmun inscription, providing valuable insight into the site's history and that of ancient Sidon. (Full article...)Selected Country Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 70 million, it spans 513,120 square kilometres (198,120 sq mi). Thailand is bordered to the northwest by Myanmar, to the northeast and east by Laos, to the southeast by Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the southwest by the Andaman Sea; it also shares maritime borders with Vietnam to the southeast and Indonesia and India to the southwest. Bangkok is the state capital and largest city. Tai peoples migrated from southwestern China to mainland Southeast Asia from the 6th to 11th centuries. Indianised kingdoms such as the Mon, Khmer Empire, and Malay states ruled the region, competing with Thai states such as the Kingdoms of Ngoenyang, Sukhothai, Lan Na, and Ayutthaya, which also rivalled each other. European contact began in 1511 with a Portuguese diplomatic mission to Ayutthaya, which became a regional power by the end of the 15th century. Ayutthaya reached its peak during the 18th century, until it was destroyed in the Burmese–Siamese War. King Taksin the Great quickly reunified the fragmented territory and established the short-lived Thonburi Kingdom (1767–1782), of which he was the only king. He was succeeded in 1782 by Buddha Yodfa Chulaloke (Rama I), the first monarch of the current Chakri dynasty. Throughout the era of Western imperialism in Asia, Siam remained the only state in the region to avoid colonization by foreign powers, although it was often forced to make territorial, trade, and legal concessions in unequal treaties. The Siamese system of government was centralised and transformed into a modern unitary absolute monarchy during the reign of Chulalongkorn (Rama V). In World War I, Siam sided with the Allies, a political decision made in order to amend the unequal treaties. Following a bloodless revolution in 1932, it became a constitutional monarchy and changed its official name to Thailand, becoming an ally of Japan in World War II. In the late 1950s, a military coup under Field Marshal Sarit Thanarat revived the monarchy's historically influential role in politics. During the Cold War, Thailand became a major ally of the United States and played an anti-communist role in the region as a member of the failed SEATO, but since 1975 it has sought to improve relations with Communist China and Thailand's neighbours. (Full article...)Featured biographyPreity G Zinta (pronounced [ˈpriːt̪i ˈzɪɳʈa]; born 31 January 1975) is an Indian entrepreneur and actress primarily known for her work in Hindi films. After graduating with degrees in English honours and criminal psychology, Zinta made her acting debut in Dil Se.. in 1998, followed by a role in Soldier in the same year. These performances earned her the Filmfare Award for Best Female Debut, and she was later recognised for her role as a teenage single mother in Kya Kehna (2000). She subsequently established a career as a leading actress of Hindi cinema with a variety of character types. Her roles, often deemed culturally defiant, along with her unconventional screen persona won her recognition and several accolades. Following critically appreciated roles in Chori Chori Chupke Chupke (2001), Dil Chahta Hai (2001), Dil Hai Tumhaara (2002), and Armaan (2003), Zinta received the Filmfare Award for Best Actress for her performance in Kal Ho Naa Ho (2003). She starred in two consecutive annual top-grossing films in India, Koi... Mil Gaya (2003) and Veer-Zaara (2004), and was noted for her portrayal of independent, modern Indian women in Salaam Namaste (2005) and Kabhi Alvida Naa Kehna (2006), top-grossing productions in domestic and overseas markets. For her first international role in the Canadian drama Heaven on Earth (2008) she was awarded the Silver Hugo Award for Best Actress and nominated for the Genie Award for Best Actress. She followed this with a hiatus from acting work for several years, with the exception of her self-produced comeback film, Ishkq in Paris (2013), which failed to leave a mark. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured pictureView of one of the Yeddi Gumbez Mausoleums at dusk in Şamaxı, Azerbaijan. The cemetery dates from 1810 and was built for a family of Mustafa khan – the last khan of Shamakhi.
Did you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Surroundings Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
The Central Area of Singapore surrounded by the perimeter of five planning areas: the Marina Bay, the Downtown Core, Marina East, Marina South and Straits View. The area surrounding the bay itself, also called Marina Bay, is a 360 hectare extension to the adjacent CBD. It is also the new downtown of Singapore built on reclaimed land. TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA Purge server cache |






























































































