Portal:Volcanoes
The Volcanoes portal

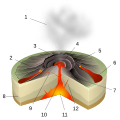
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 kilometers (1,900 mi) deep within Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.
Large eruptions can affect atmospheric temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the Sun and cool Earth's troposphere. Historically, large volcanic eruptions have been followed by volcanic winters which have caused catastrophic famines.
Other planets besides Earth have volcanoes. For example, volcanoes are very numerous on Venus. In 2009, a paper was published suggesting a new definition for the word ‘volcano’ that includes processes such as cryovolcanism. It suggested that a volcano be defined as ‘an opening on a planet or moon’s surface from which magma, as defined for that body, and/or magmatic gas is erupted.’
This article mainly covers volcanoes on Earth. See § Volcanoes on other celestial bodies and Cryovolcano for more information. (Full article...)
Selected article -
On March 27, 1980, a series of volcanic explosions and pyroclastic flows began at Mount St. Helens in Skamania County, Washington, United States. A series of phreatic blasts occurred from the summit and escalated until a major explosive eruption took place on May 18, 1980, at 8:32 am. The eruption, which had a volcanic explosivity index of 5, was the first to occur in the contiguous United States since the much smaller 1915 eruption of Lassen Peak in California. It has often been declared the most disastrous volcanic eruption in U.S. history.
The eruption was preceded by a two-month series of earthquakes and steam-venting episodes caused by an injection of magma at shallow depth below the volcano that created a large bulge and a fracture system on the mountain's north slope. An earthquake at 8:32:11 am PDT (UTC−7) on May 18, 1980, caused the entire weakened north face to slide away, a sector collapse which was the largest subaerial landslide in recorded history. This allowed the partly molten rock, rich in high-pressure gas and steam, to suddenly explode northward toward Spirit Lake in a hot mix of lava and pulverized older rock, overtaking the landslide. An eruption column rose 80,000 feet (24 km; 15 mi) into the atmosphere and deposited ash in 11 U.S. states and various Canadian provinces. At the same time, snow, ice, and several entire glaciers on the volcano melted, forming a series of large lahars (volcanic mudslides) that reached as far as the Columbia River, nearly 50 miles (80 km) to the southwest. Less severe outbursts continued into the next day, only to be followed by other large, but not as destructive, eruptions later that year. The thermal energy released during the eruption was equal to 26 megatons of TNT. (Full article...)Did you know
- ... that The Volcano (pictured) in northwestern British Columbia is the youngest known volcano in Canada, and its last eruption likely took place only 150 years ago?
- ... that the Geology of the Northland Region, New Zealand, includes exotic seafloor rocks, an extinct volcanic arc, and a massive tombolo?
- ... that volcanic eruptions may have contributed to the population decline of the Pink-headed warbler?
- ... that CenSeam is an initiative to biologically sample seamounts (submarine volcanoes), of which about 100,000 exist and only 350 have received attention?
- ... that the Graveyard Seamounts are all named morbidly, with names such as Pyre Seamount, Morgue Seamount, and Zombie Seamount?
- ... that the tablemount structure of Sedlo Seamount, a seamount (submarine volcano), indicates that it used to be above the water?
- ... that observations and samplings from Jasper Seamount show that it is very similar to Hawaiian volcanoes?
- ... that South Chamorro Seamount, a submarine mud volcano near the Mariana Trench, is only the second such structure in the world to be sampled?
General images
Selected biography -

Selected picture
 |
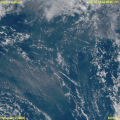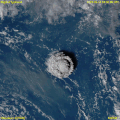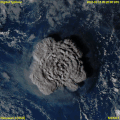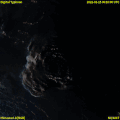
An October 2002 eruption of Mount Etna, a volcano on the Italian island of Sicily, as seen from the International Space Station. Etna is the largest of Italy's three active volcanoes and one of the most active in the world. This eruption, one of Etna's most vigorous in years, was triggered by a series of earthquakes. Ashfall was reported as far away as Libya, 600 km (373 mi) to the south.
Selected quote
"We'll just look at you. If you looked scared then we'll panic."
— Discovery channel crew, talking to volcanologist John Seach during filming at Yasur Volcano, 2000.
Related portals
WikiProjects
Volcanoes topics
Subcategories
Featured work and other approved content

Featured articles: 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens • 2007–2008 Nazko earthquakes • Amchitka • Armero tragedy • Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve • Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) • David A. Johnston • Enceladus (moon) • Geology of the Lassen volcanic area • Io (moon) • Kamaʻehuakanaloa Seamount • Mauna Kea • Mauna Loa • Metacomet Ridge • Mono-Inyo Craters • Mount Cayley volcanic field • Mount St. Helens • Mount Tambora • Nevado del Ruiz • Surtsey • The Volcano (British Columbia) • Triton (moon) • Upper and Lower Table Rock • Volcanism on Io • Volcano (South Park) • Yellowstone National Park
Featured lists: List of volcanoes in Indonesia • List of volcanoes in the Hawaiian – Emperor seamount chain • List of largest volcanic eruptions
Featured pictures: There are currently 43 volcano-related Featured pictures. A full gallery can be seen here.

Good articles: Abyssal plain • Amak Volcano • Anahim hotspot • Axial Seamount • Ben Nevis • Bowie Seamount • Crater Lake • Davidson Seamount • Ferdinandea • Gareloi Volcano • Geyser • Glacier Peak • Hawaii hotspot • Hualālai • Kohala (mountain) • Lake Toba • Minoan eruption • Mount Adams (Washington) • Mount Bailey • Mount Baker • Mount Cleveland (Alaska) • Mount Edziza volcanic complex • Mount Garibaldi • Mount Hood • Mount Kenya • Mount Rainier • Mount Redoubt • Mount Tehama • Mount Thielsen • Mount Vesuvius • Peter I Island • Roxy Ann Peak • Rùm • Sakurajima • Sangay • Silverthrone Caldera • Staffa • Types of volcanic eruptions • Volcanic ash • Weh Island • Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field • Yamsay Mountain
Valued pictures: A gallery of volcano-related valued pictures can be seen here.
What you can do

- Add the {{WikiProject Volcanoes}} message box to talk pages of articles within the scope of this project, including appropriate assessments, if needed.
- Add appropriate volcano type categories to articles, and verify the accuracy of any existing categories. See the section "Categorization" below.
- Add {{infobox mountain}} to articles if needed and missing, and add volcano-related fields to existing infoboxes if these are missing.
- Expand volcano articles which are stubs, especially by adding photos and (most importantly) proper references.
- Help improve articles related to Hawaiian and Canadian volcanism by joining the Hawaiian and Canadian workgroups.
- Improve some of the project's most visible articles.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus